TLDRs;
Contents
- Nvidia posted record $46.7B revenue, up 56%, but stock dipped 5% on weak China sales before stabilizing later.
- China revenue fell 24% to $2.8B as US export rules and Beijing’s policies squeezed Nvidia’s market access.
- CEO Jensen Huang warned that China’s $50B AI market is shifting toward domestic competitors amid trade tensions.
- Despite explosive growth from rivals like Cambricon, Nvidia’s scale and global dominance still dwarf emerging challengers.
Nvidia Corp. (NVDA) stock dipped more than 5% in after-hours trading on Thursday, despite the company reporting blockbuster quarterly earnings.
The selloff was triggered by fresh warnings over its China business, a market facing mounting headwinds from both U.S. trade restrictions and Beijing’s push for local alternatives. Shares later regained some ground, ending the week relatively stable.
The chipmaker’s revenue soared 56% year-on-year to $46.7 billion for the quarter ended July 27, underscoring Nvidia’s dominance in the booming artificial intelligence sector. Despite this financial strength, geopolitical friction and weakening demand in China weighed heavily on investor sentiment.
China revenue slides sharply
Revenue from China, including Hong Kong, plunged 24% to $2.8 billion, a sharp reversal for what has historically been one of Nvidia’s largest markets.
The company also disclosed that it recorded no sales of its H20 chips, a line specifically designed for Chinese buyers under US export restrictions, compared with $4.6 billion in sales the prior quarter.
🚨 $NVDA Q2 Earnings 🚨
• Total Sales $46.7B vs Est. $46.1B
• EPS $1.05 vs Est. $1.01
• Data Center Sales $41.1B vs Est. $41.3B
• Networking Sales $5.1B vs Est. $5.1BQ3 Guidance
• Sales $54B vs Est. $46B
• Gross Margins 74% vs. Est. 72%Nvidia approves additional $60B… pic.twitter.com/djPmaakYQA
— Shay Boloor (@StockSavvyShay) August 27, 2025
This steep decline highlights how both US trade controls and Chinese policy measures are accelerating a semiconductor bifurcation. Nvidia remains squeezed between regulatory pressures in Washington and Beijing’s push for homegrown alternatives, leaving a once-lucrative market increasingly out of reach.
A $50 billion opportunity at risk
Chief Executive Jensen Huang acknowledged that China represents a $50 billion market opportunity and is home to half the world’s AI researchers. Yet he cautioned that Chinese government policies are steering local buyers toward domestic competitors, further complicating Nvidia’s long-term outlook.
Beijing’s promotion of self-sufficiency is already showing results. China’s semiconductor index has surged 32% in 2025, reflecting government incentives and growing investment in local chip design firms.
Simultaneously, China has restricted exports of gallium and germanium, two essential materials for semiconductor manufacturing, signaling its willingness to leverage supply chains in response to Western restrictions.
Global rivalry, domestic competition
While Chinese startups like Cambricon Technologies have posted eye-popping percentage growth, up more than 4,300% year-on-year, their absolute scale remains small compared to Nvidia. Cambricon reported $403 million in first-half revenue, a fraction of Nvidia’s $44 billion over the same period.
Analysts note that such dramatic growth percentages can mask how difficult it is for challengers to erode the dominance of entrenched players. Still, the trend underscores a broader realignment of the semiconductor industry, where domestic champions in China are receiving increasing support to compete with global leaders.
Market reaction and outlook
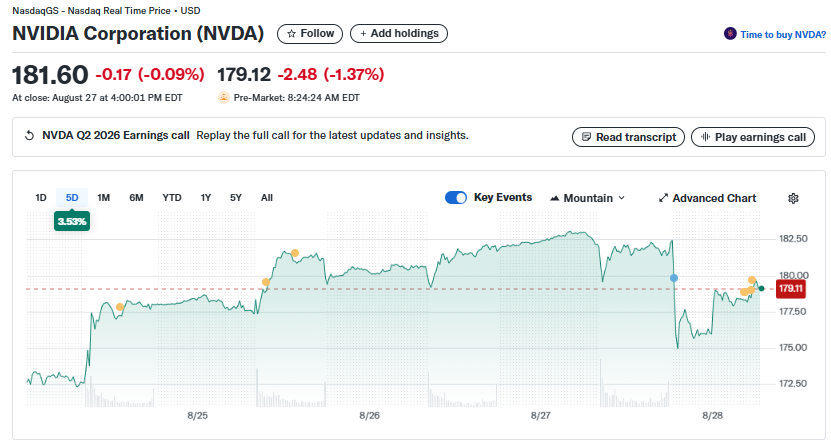
Nvidia’s stock closed at $181.60 before its earnings release but dropped to $172.45 in after-hours trading as investors digested the China warning.
The decline was later pared as markets reopened, reflecting investor confidence in Nvidia’s fundamentals despite geopolitical turbulence.
While the company’s global dominance in AI chips remains intact, the China dilemma highlights risks ahead. With supply chain control, regulatory headwinds, and domestic competition all converging, Nvidia must balance compliance with US rules while maintaining access to a strategically vital market.


